Core Standards and Primary Categories of Industrial Power Modules
Date:2025-03-31 Publisher:BettpowerAs the “power heart” of modern industry, industrial power modules must not only withstand harsh environments like extreme temperatures and severe vibrations but also perform precise energy conversion within milliseconds. Industry statistics indicate that approximately 23% of industrial equipment failures are related to power systems, while power modules meeting core standards can reduce failure rates by over 60%. Below is a brief introduction to the core standards and primary classifications of industrial power modules, providing engineers with key decision-making criteria for selection.
I. Primary Categories of Industrial Power Modules
1. Classification by Input/Output Type
— AC/DC Power Modules: Input: AC power (85~265VAC or three-phase four-wire 380VAC); Output: Stabilized DC power. Suitable for mains-powered applications (e.g., PLC control systems, industrial computers).
— DC/DC Power Modules: Input is DC power (e.g., 24VDC), output provides multiple DC voltage specifications, meeting distributed power supply needs (e.g., secondary power supplies in power systems, automotive electronics).
— DC/AC Inverter Modules: Convert DC power to AC power, suitable for specialized motor drives or emergency backup power supplies.
2. Classification by Power Rating
— Low-power modules (0.1–30W): Compact and cost-effective for low-power applications like sensors and portable instruments.
— Medium-power modules (50–200W): Balancing efficiency and thermal management for medium-load equipment such as industrial controls and communication base stations.
— High-power modules (200W+): Require enhanced thermal design and support high-density integration for large industrial equipment and power systems.
3. Classification by Functional Characteristics
— Voltage-stabilizing modules: Stabilize output voltage via negative feedback, resisting input fluctuations and load surges, suitable for precision instruments.
— Isolation Modules: Provide 1500–6000VDC electrical isolation between input/output, used in high-reliability scenarios like ground loop elimination and lightning protection.
— Adjustable Modules: Support manual adjustment of output voltage or current to accommodate flexible power supply requirements.
4. Classification by Technical Principle
— Linear Power Modules: Low noise and ripple but with efficiency ranging from 30% to 60%. Suitable for low-power applications such as medical equipment and laboratory instruments.
— Switching Power Modules: Achieve efficiency between 70% and 95% with compact size. Requires high-frequency noise suppression and is widely used in medium-to-high power industrial equipment.
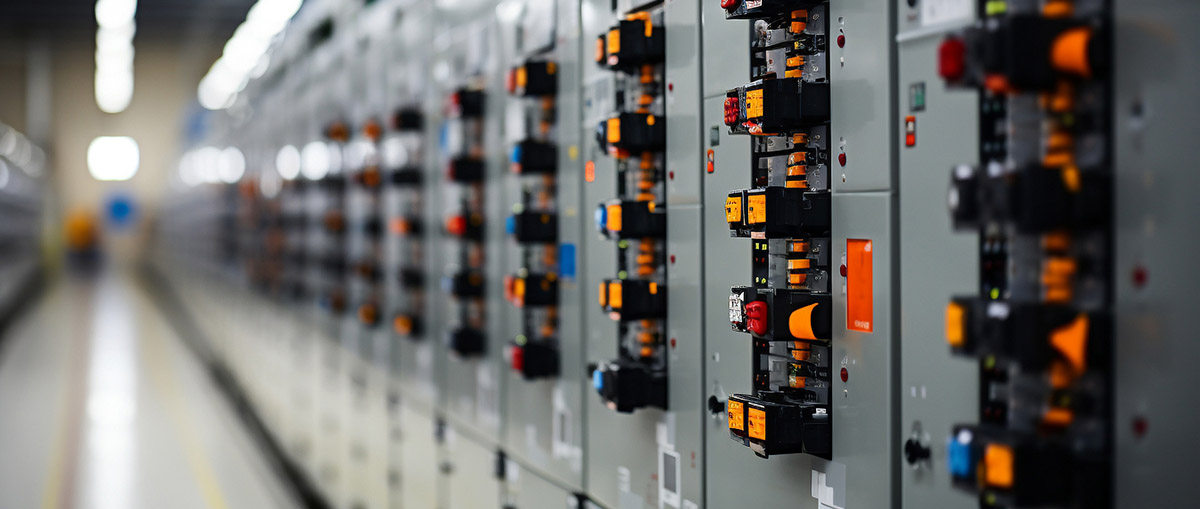

II. Core Standards for Industrial Power Modules
1. Harsh Environment Adaptability
— Wide Temperature Operation: Industrial-grade modules must support -40°C to +85°C operating temperatures, with extreme scenarios (e.g., aerospace, petroleum) requiring -55°C to +125°C.
— Vibration and Moisture Resistance: Compliant with IEC 60068 standards, withstanding vibration, humidity, and salt spray corrosion to adapt to complex industrial field conditions.
2. Hard Electrical Performance Metrics
— Wide Input Range: AC input compatible with 85–265 VAC; DC input supporting an ultra-wide range of 9–36 VDC to handle grid fluctuations.
— High Isolation Voltage: Industrial applications require minimum 1500VDC isolation; critical sectors like power systems demand 3000–6000VDC isolation.
— Efficiency & Derating Design: Recommended load rate is 30–80% of rated power; derating is required in high-temperature environments to extend service life.
3. Safety & Certification Requirements
— Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Pass IEC 61000 series tests (e.g., surge, conducted interference) to ensure device compatibility.
— Protection Rating: Enclosures must meet IP67 (dustproof and waterproof) or higher for outdoor, dusty, or harsh environments.
4. Reliability Verification System
— Life Testing: Validate module stability under long-term full-load conditions per MIL-STD-883 or GJB 548 standards.
— Dynamic Response Capability: Output voltage recovery time must be sub-millisecond during load step changes to ensure instantaneous power supply.
Selecting industrial power modules requires comprehensive consideration of environmental adaptability, electrical performance, and industry certifications while aligning with modular and high-integration technology trends. Enterprises that precisely match module performance to application requirements—such as wide-temperature tolerance, dynamic response, and multi-certification—can not only mitigate the risk of “small power sources causing major outages” but also seize technological leadership in emerging fields like industrial IoT and digital twins.
Prev: No more.
Next: No more.

















 Sample
Sample
 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 TOP
TOP